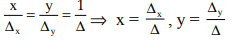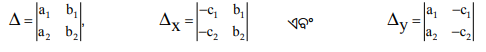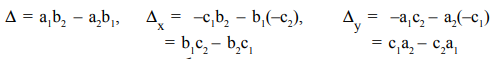Theory Note, Formulas, Solution Note and Quiz of Algebra Exercise – 1 (B) Class 10th Odia
Substitution Method ପ୍ରତିକଳ୍ପନ ପଦ୍ଧତି
- ଯେକୌଣସି ଏକ ସମୀକରଣକୁ ସଜାଡି x କୁ y ମାଧ୍ୟମରେ(ବା y କୁ x ମାଧ୍ୟମରେ) ପ୍ରକାଶ କରିବା
- Rearrange one of the given equations to express x in terms of y
- ଏବେ y ରୂପରେ ଥିବା x ର ମାନକୁ ଦ୍ଵିତୀୟ ସମୀକରଣରେ ବ୍ୟବହାର କଲେ ଆମେ y ର ପାଇଁ ସମୀକରଣକୁ ସମାଧାନ କରିପାରିବା
- Now, the expression for x can be substituted in the other equation to find the value of y.
- ଏବେ y ର ମାନକୁ ପ୍ରଥମ ସମୀକରଣରେ ବ୍ୟବହାର କାଲେ x ର ମାନ ନିର୍ଣ୍ଣୟ କରିହେବ ।
- Finally, substitute the value of y in any of the equations to find the value of x.
ଉଦାହରଣ
3x – 4y = 0 (i)
9x – 8y = 12 (ii)
- Step 1 : ସମୀକରଣ (i)ରେ x କୁ y ରୂପରେ ପ୍ରକାଶ କରିବା
- 3x = 4y
- =>x = 4/3 y
- Step 2 : x ର ମାନକୁ ସମୀକରଣ (ii)ରେ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରିବା
- 9 (4/3)y – 8y = 12
- =>12y – 8y = 12
- => 4y = 12
- => y = 3
- Step 3 : y ର ମନକୁ ସମୀକରଣ (i) ରେ ବ୍ୟବହାର କରି x ପାଇଁ ସମାଧାନ କରିବା
- x = 4/3y
- => x = 4/3 (3) = 4
x, y ର ମାନ ପ୍ରତିକଳ୍ପନ ପଦ୍ଧତିରେ ଆମେ 4,3 ପାଇଲୁ
Elimination Method ଅପସାରଣ ପଦ୍ଧତି
- ଦୁଇଟି ସମୀକରଣର ଯେ କୌଣସି ଏକ ଅଜ୍ଞାତରଶୀର ସହଗକୁ ସମାନ କରିବା ପାଇଁ ଉଭୟ ସମୀକରଣକୁ ଏକ ସଂଖ୍ୟା ସହ ଗୁଣିବା ।
- Multiply the given equations by a constant, so as to make the coefficients of any one of the variables in the equations equal.
- ଏବେ ସମୀକରଣ ଦ୍ୱୟକୁ ଯୋଗ ବା ବିୟୋଗ କରି ସମସହଗ ଥିବା ଅଜ୍ଞାତରଶୀକୁ ଅପସାରଣ କରିବା
- Add or subtract the equations to eliminate the variable having the same coefficients.
- ଏବେ କେବଳ ଗୋଟିଏ ଅଜ୍ଞତାରଶୀ ପାଇଁ ସମୀକରଣକୁ ସମାଧାନ କରିବା
- Now, solve the equation for one variable.
- ମିଳିଥିବା ସମାଧାନକୁ ଯେକୌଣସି ସମୀକରଣରେ ପ୍ରୟୋଗ କରି ଅନ୍ୟ ଅଜ୍ଞାତରଶୀର ସମାଧାନ ପାଇ ପାରିବା
- Substitute the variable value in any of the equations to find the value of the other variable.
ଉଦାହରଣ
ସମାଧାନ କର
2x + 3y – 8 = 0 (i)
3x + y – 5 = 0 ()
- 3x(ii) =>9x +3y-15 = 0
- (ii) – (i) 9x-2x+3y-3y-15-(-8) = 0
- =>7x-7= 0
- => x = 1 …….. (iii)
- put x=1in (ii)
- 3 (1) + y -5 = 0
- => y = 5-3 = 2
(x,y) = (1,2)
Cross Multiplication ବଜ୍ର ଗୁଣନ
ଯଦି ଦୁଇଟି ସରଳସହସମୀକରଣ a1x + b1 y +c1 = 0 ଏବଂ a2x + b2 y +c2 = 0 ହୁଅନ୍ତି ତେବେ ବଜ୍ରଗୁଣନ ସୂତ୍ର ଅନୁସାରେ ତାଙ୍କ ସମାଧାନ
If two linear Simultaneous Equations are a1x + b1 y +c1 = 0 and a2x + b2 y +c2 = 0 then the solution is
x = (b1c2 – b2c1) / (a1b2 – a2b1)
y =(c1a2 – c2a1) / (a1b2 -a2b1)
Important ଦ୍ରଷ୍ଟବ୍ୟ
- ଯଦି c1 = c2 = 0 ଏବଂ a1b2 -a2b1 ≠ 0 ହେଲେ ସମୀକରଣ ଦ୍ୱୟର ସମାଧାନ (0,0) ହେବ । ସମୀକରଣ ଦ୍ୱୟଙ୍କୁ ସମସହସମୀକରଣ କୁହାଯିବ ।
- If c1 = c2 = 0 and a1b2 -a2b1 ≠ 0 , then the solution of the two equation is (0,0) । The two equations are said to be Homogenuous Simultaneous Equation.
Example ଉଦାହରଣ
ସମାଧାନ କରିବା 2x – 3y –1 = 0, 4x + y – 9 = 0
ଏଠାରେ a1 = 2, b1 = -3, c1 = -1, a2 = 4, b2 = 1, c2 = -9
x = (b1c2 – b2c1) / (a1b2 – a2b1)
- = (-3)(-9) – 1(-1) / 2.1 – 4(-3)
- = 27+1/ 2+12 = 28/14
- => x = 2
y =(c1a2 – c2a1) / (a1b2 -a2b1)
- = (-1)4 -(-9)2 / 2.1 – 4(-3)
- = -4+18/14 = 14/14
- => y = 1
Cramer’s Rule
ବଜ୍ର ଗୁଣନ ହିଁ Cramer’s Rule.
Cross multiplication formula is based on Cramer’s Rule.